Cannon-Fenske opaque viscometers
Used for the determination of kinematic viscosity of liquid asphalts (bitumens) and road oils at 60°C and distillation residue of liquid asphalts and asphalt cements at 135°C. Cannon-Fenske Opaque models are suitable for opaque liquids. Supplied complete with calibration certificate.
Zeitfuchs cross-arm viscometers
Used for the determination of kinematic viscosity of liquid asphalts (bitumens) road oil and distillation residues of liquid asphalts and asphalt cements at 135°C. Supplied complete with calibration certificate.
BS U-Tube modified reverse flow viscometers
Used for the determination of kinematic viscosity of liquid asphalts (bitumen) road oil and distillation residues of liquid asphalts and asphalt cements at 135°C. Supplied complete with calibration certificate.
For determining the kinematic viscosity, all the above viscometers have to be introduced in the 81-B0116/A Viscometer bath by the appropriate Holder 81-B0116/H2 for Zeitfuchs cross-arm models and 81-B0116/H3 for BS U-Tube models.
See accessories.
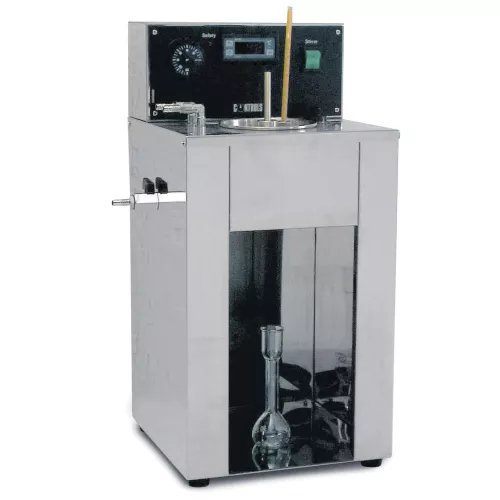
Viscometer bath is used in the determination of both the kinematic and dynamic viscosity. Used to maintain the
capillary type viscometers at a uniform temperature. The bath consists of a cylindrical glass vessel with a stainless steel cover with 50.8 mm diameter holes, motor stirrer, refrigerating coil with water connections, heating system, contact thermometer, external protection and insulating base. NOTE: 81-PV0116/A viscometer bath includes six holders for Cannon-Fenske viscometers.